Autonomic Nervous System Effectors
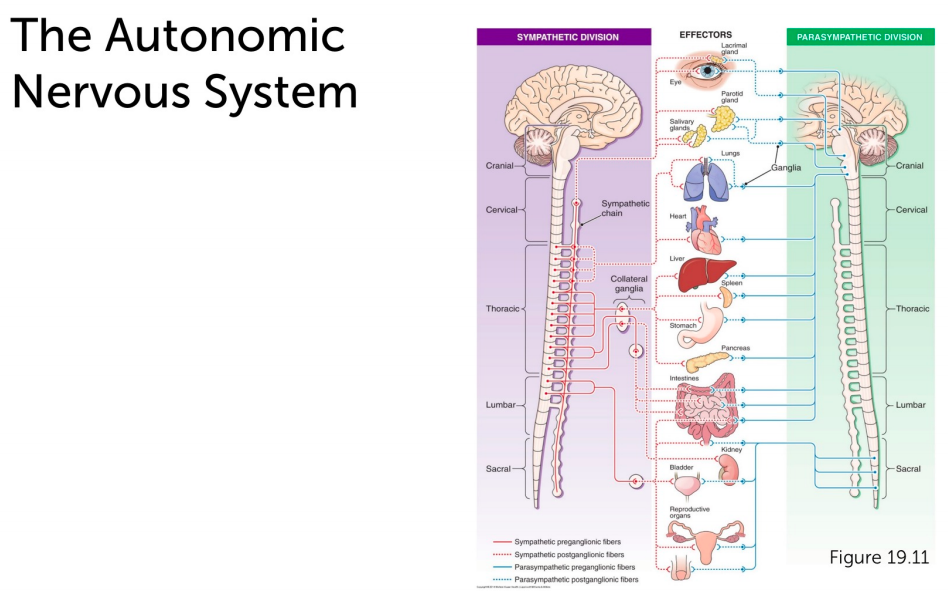
Autonomic nervous system effectors. Autonomic nervous system inervates. Effectors of the autonomic nervous system include smooth muscles of blood vessels cardiac muscle and various glands throughout the body. Autonomic nervous system is an involuntary system that primarily controls and modulates the functions of the visceral organs.
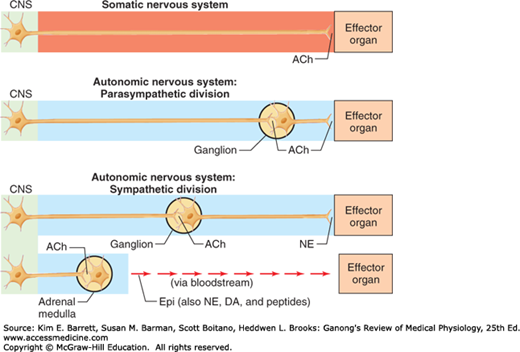
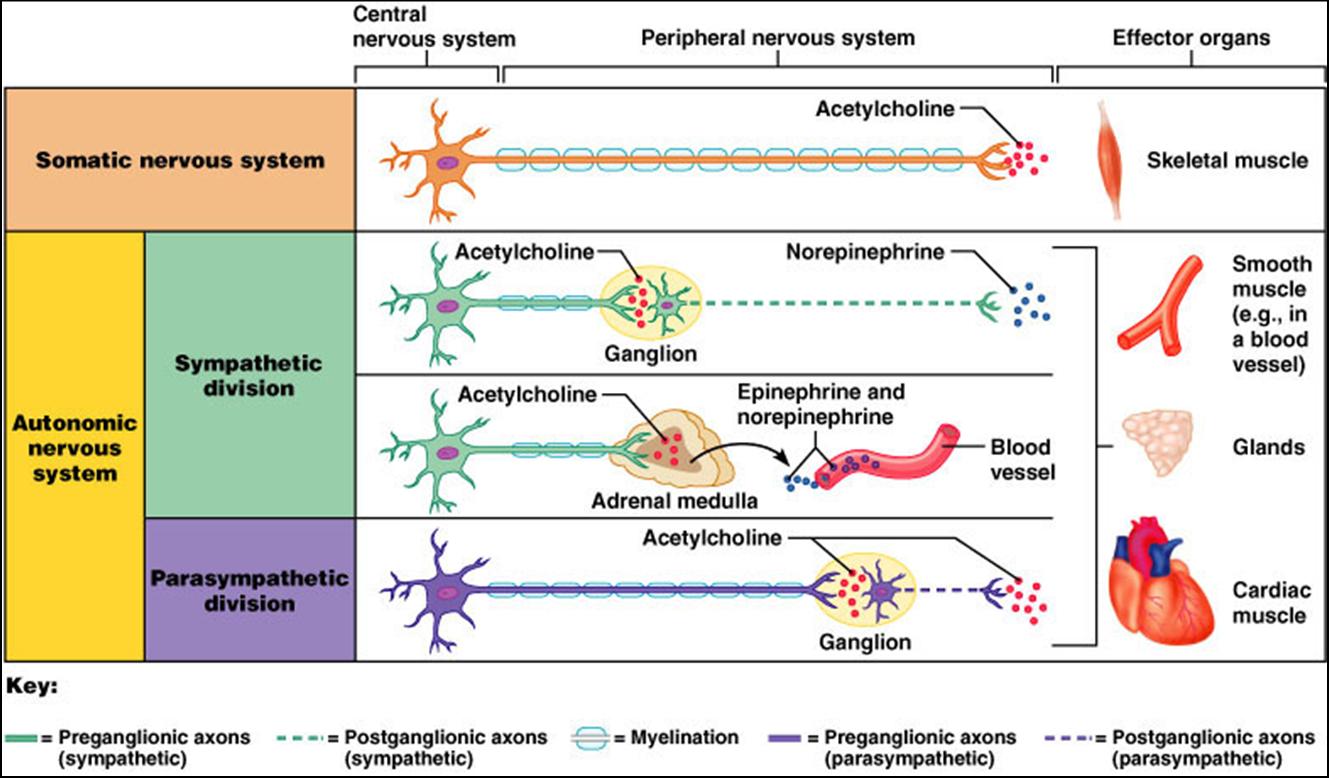
Autonomic ganglion and 2 efferent neurons in series link the CNS to visceral effectors. The peripheral nervous system consists of the somatic nervous system SNS and the autonomic nervous system ANS. Autonomic motor nerves innervate organs whose functions are not usually under voluntary control.
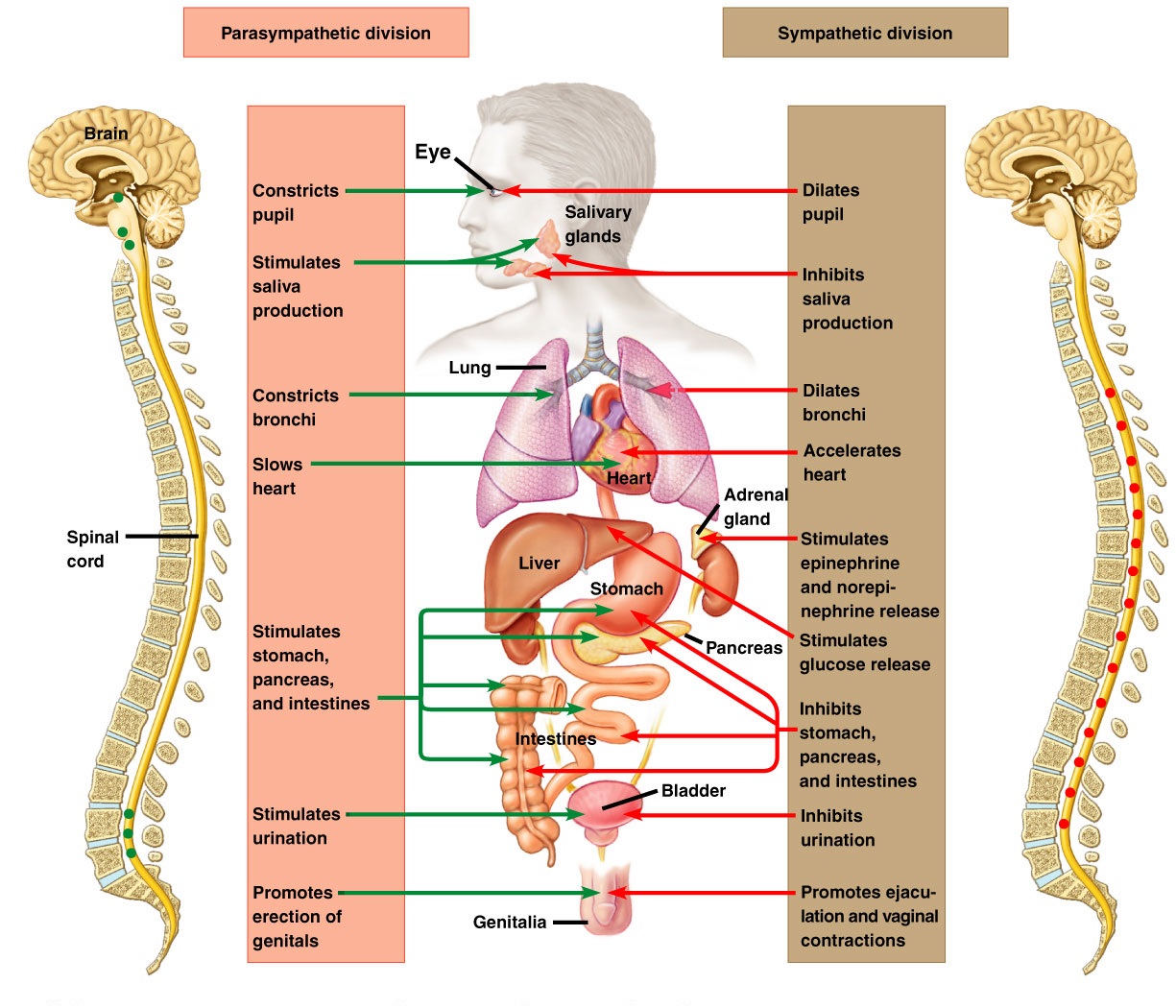
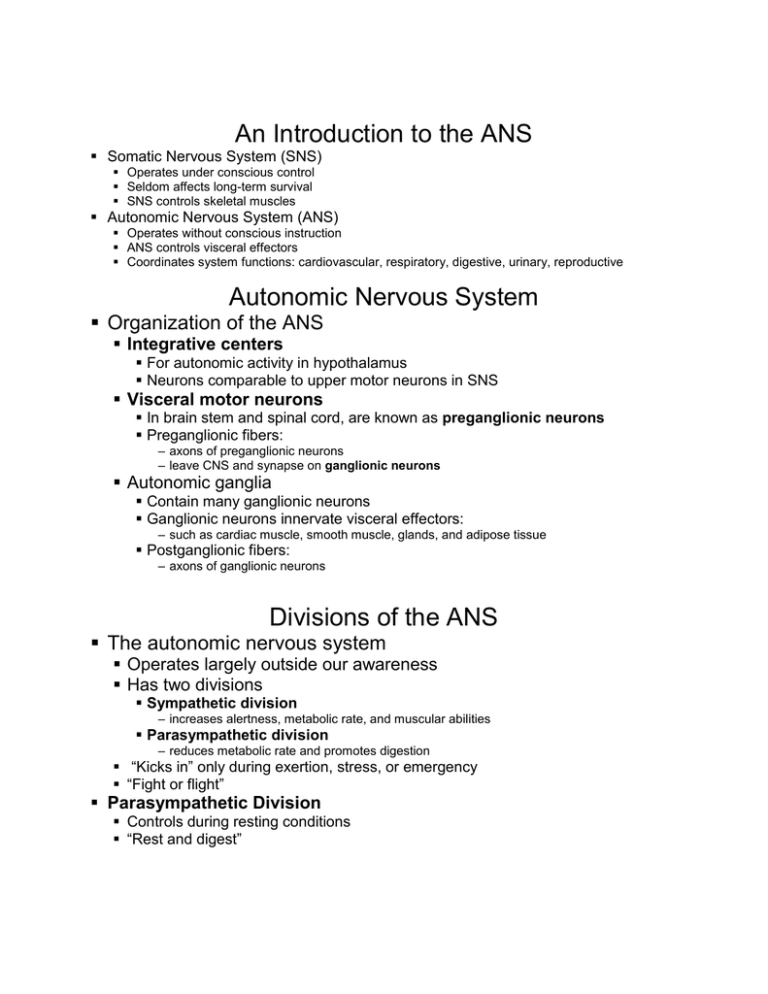
The autonomic nervous system ANS is a subdivision of the nervous system that regulates involuntary effectors Figure 16-1. What is neurotransmitter for autonomic nervous system. Because it controls involuntary effectors we can think of the autonomic system as our system of subconscious regulation of body functions.
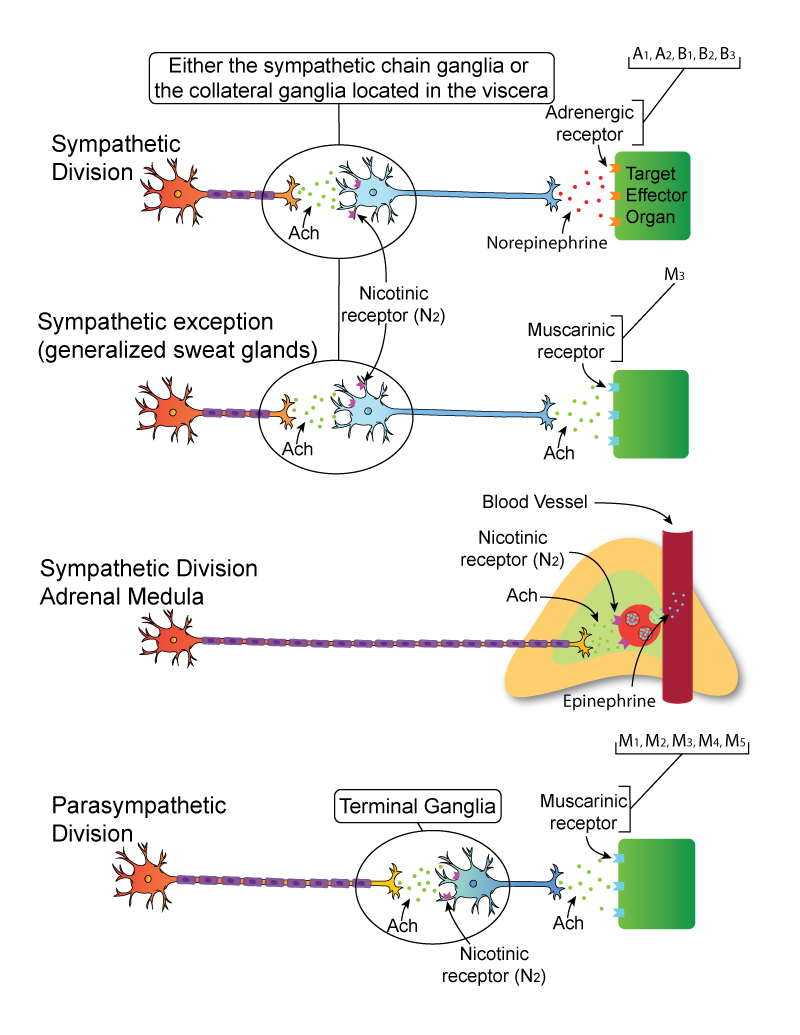
Certain drugs exert their effects by binding to cholinergic and adrenergic receptors to increase or decrease the activity of effectors normally controlled by the ANS. There are two branches or divisions of the autonomic nervous system ANS. Reflexes and we now turn to the autonomic nervous system ANS and visceral reflexes reflexes that regulate such primitive functions as blood pressure heart rate body temperature diges-.
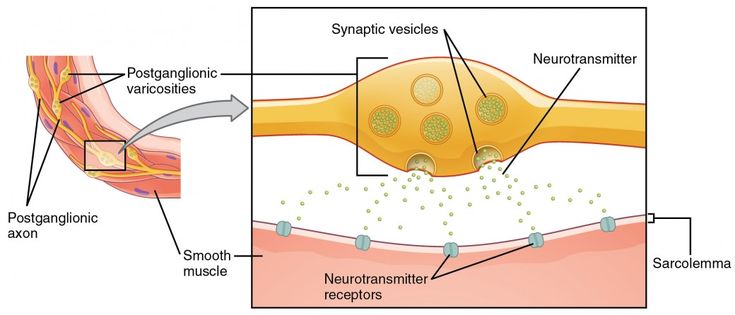
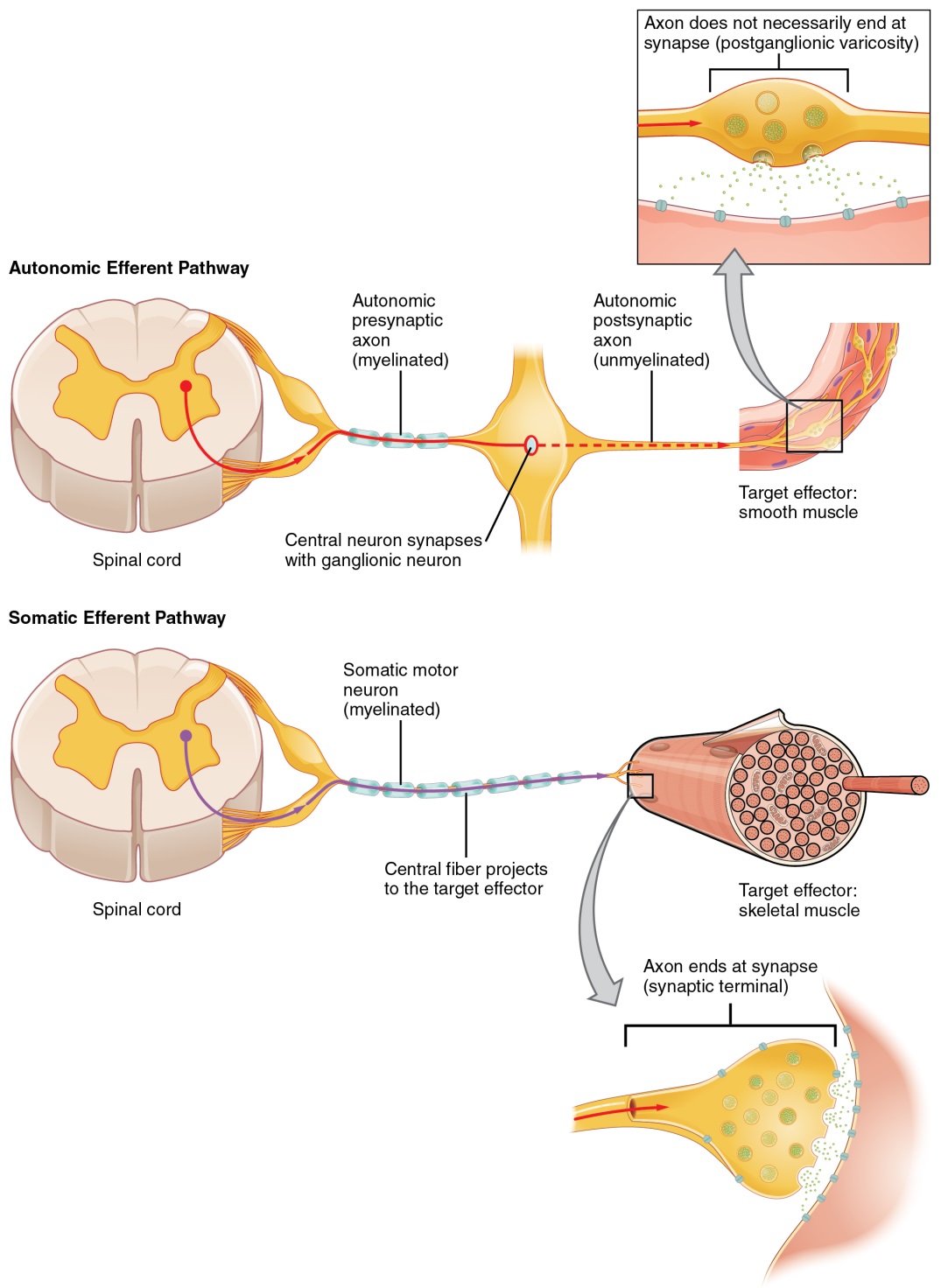
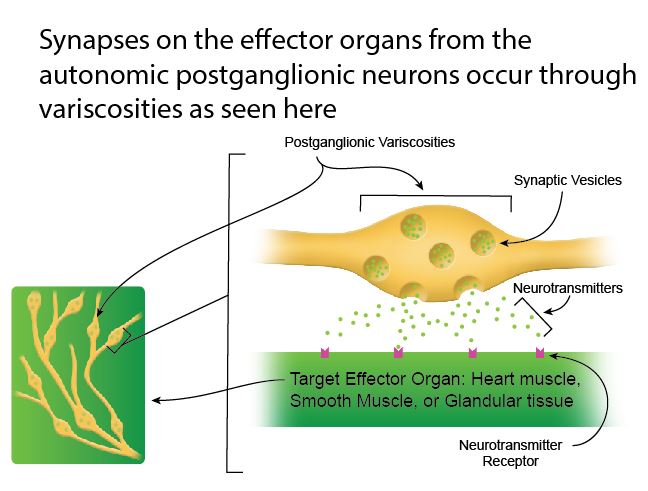
The effectors of the somatic nervous system are the skeletal muscles. Describe how the neuroeffector junction in the autonomic nervous system differs from that of a neuron-to-neuron synapse. Autonomic Nervous System ANS Study Guide List another name for the ANS and describe how that name exemplifies its function - Also called visceral motor system regulates what happens inside body are automatic and are involuntary List the organs that are controlled by the ANS - Glands sweat glands sebaceous glands endocrine glands salivary glands - Cardiac muscle - Smooth.
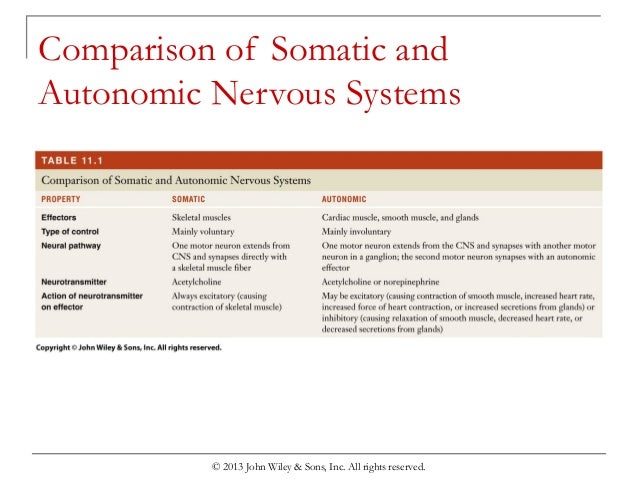
Explain how the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system connect the CNS to effectors be sure to include structural and functional components. The autonomic nervous system is a component of the peripheral nervous system that regulates involuntary physiologic processes including heart rate blood pressure respiration digestion and sexual arousal. The SNS consists of motor neurons that stimulate skeletal muscles.
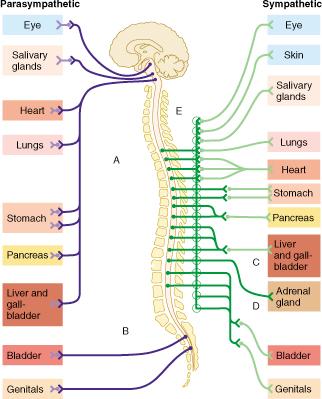
-effectors in body wall are innervated by sympathetic fibers in spinal nerves-effectors in head and thoracic cavity are innervated by fibers in sympathetic nerves-effectors in abdominal cavity are innervated by sympathetic fibers in splanchnic nerves. Compare and contrast the anatomical features of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
Innervate smooth and cardiac muscle and glands Make adjustments to ensure optimal support for body activities Operate via subconscious control Have viscera as most of their effectors ANS in the Nervous System.
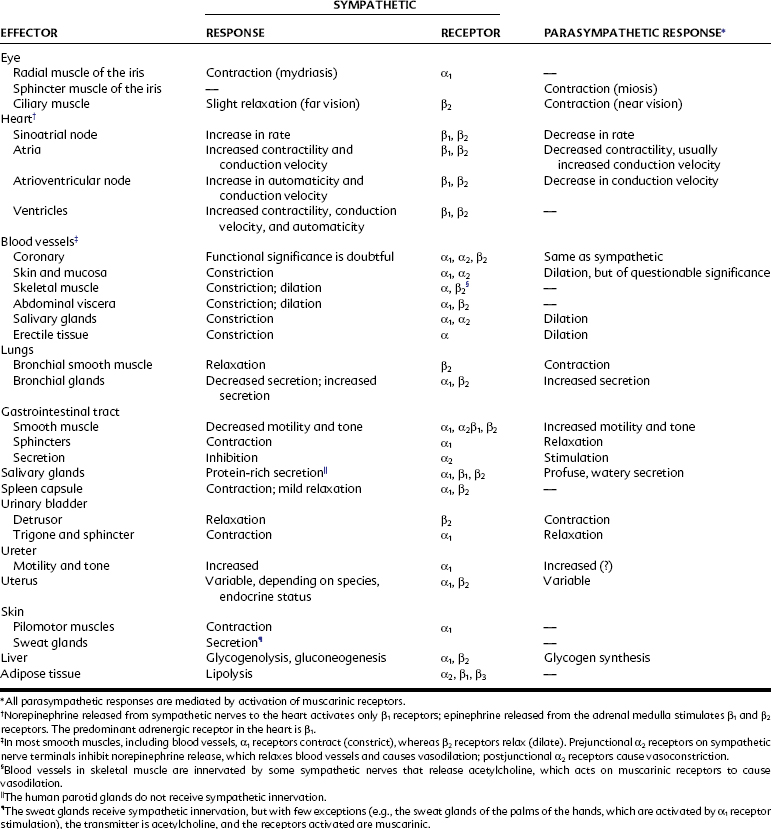
There are two branches or divisions of the autonomic nervous system ANS. The autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system ANS is a subdivision of the nervous system that regulates involuntary effectors Figure 16-1. The enteric nervous system regulates the activity of the digestive tract and functions completely independently of the CNS. The Autonomic Nervous System. Innervate smooth and cardiac muscle and glands Make adjustments to ensure optimal support for body activities Operate via subconscious control Have viscera as most of their effectors ANS in the Nervous System. Actions of the Autonomic Nervous System Receptors located on effectors their actions and drugs used to modify their activity. Because it controls involuntary effectors we can think of the autonomic system as our system of subconscious regulation of body functions. It is autonomic because it functions subconsciously and involuntarily.
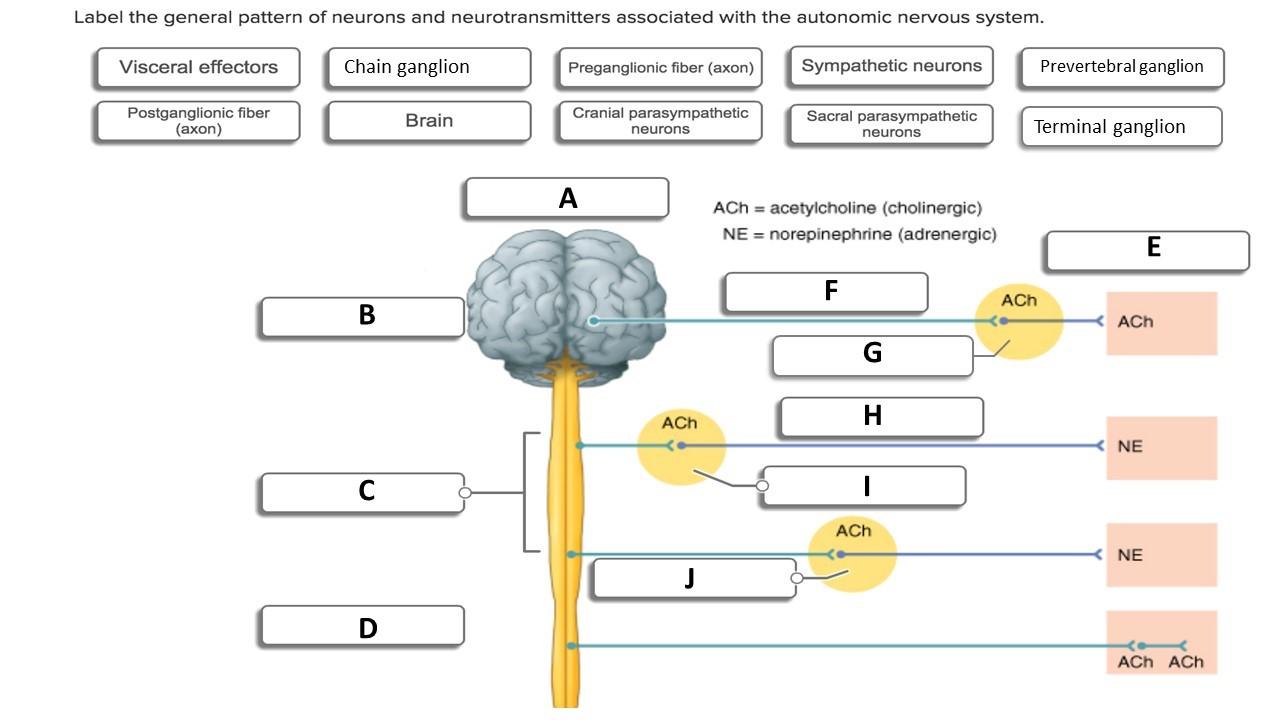
The autonomic nervous system ANS is a subdivision of the nervous system that regulates involuntary effectors Figure 16-1. The effectors of the somatic nervous system are the skeletal muscles. Autonomic motor nerves innervate organs whose functions are not usually under voluntary control. It is autonomic because it functions subconsciously and involuntarily. The peripheral nervous system consists of the somatic nervous system SNS and the autonomic nervous system ANS. The enteric nervous system regulates the activity of the digestive tract and functions completely independently of the CNS. For each neurotransmitter in the autonomic nervous system list the neurons that release them and the type and location of receptors that bind with them.























Post a Comment for "Autonomic Nervous System Effectors"